
Generally, volunteers must be screened so as to get a set of characteristics suitable for the purposes of the survey (e.g. The respondents are only volunteers in this method. Unfortunately, unless the population units are truly similar, selection is subject to the biases of the interviewer and whoever happened to walk by at the time of sampling. An example of haphazard sampling is the vox pop survey where the interviewer selects any person who happens to walk by.
Haphazard sampling assumes that the population units are all alike, then any unit may be chosen for the sample. Units are selected in an arbitrary manner with little or no planning involved. The commonly used non-probability sampling methods include the following.

Therefore, data collected using non-probability sampling should be used with extra caution. However, data from non-probability sources have a few challenges with respect to data quality, including the potential presence of participation and selection bias. Some have suggested the possibility of a shift in the paradigm and traditional approach to statistics.
#Ca element and c element formula how to#
In the last few years, however, there have been some research and studies about how to apply non-probability sampling into the official statistics. In general, official statistical agencies around the world have been using probability sampling as their preferred tool to meet information needs about a population of interest.
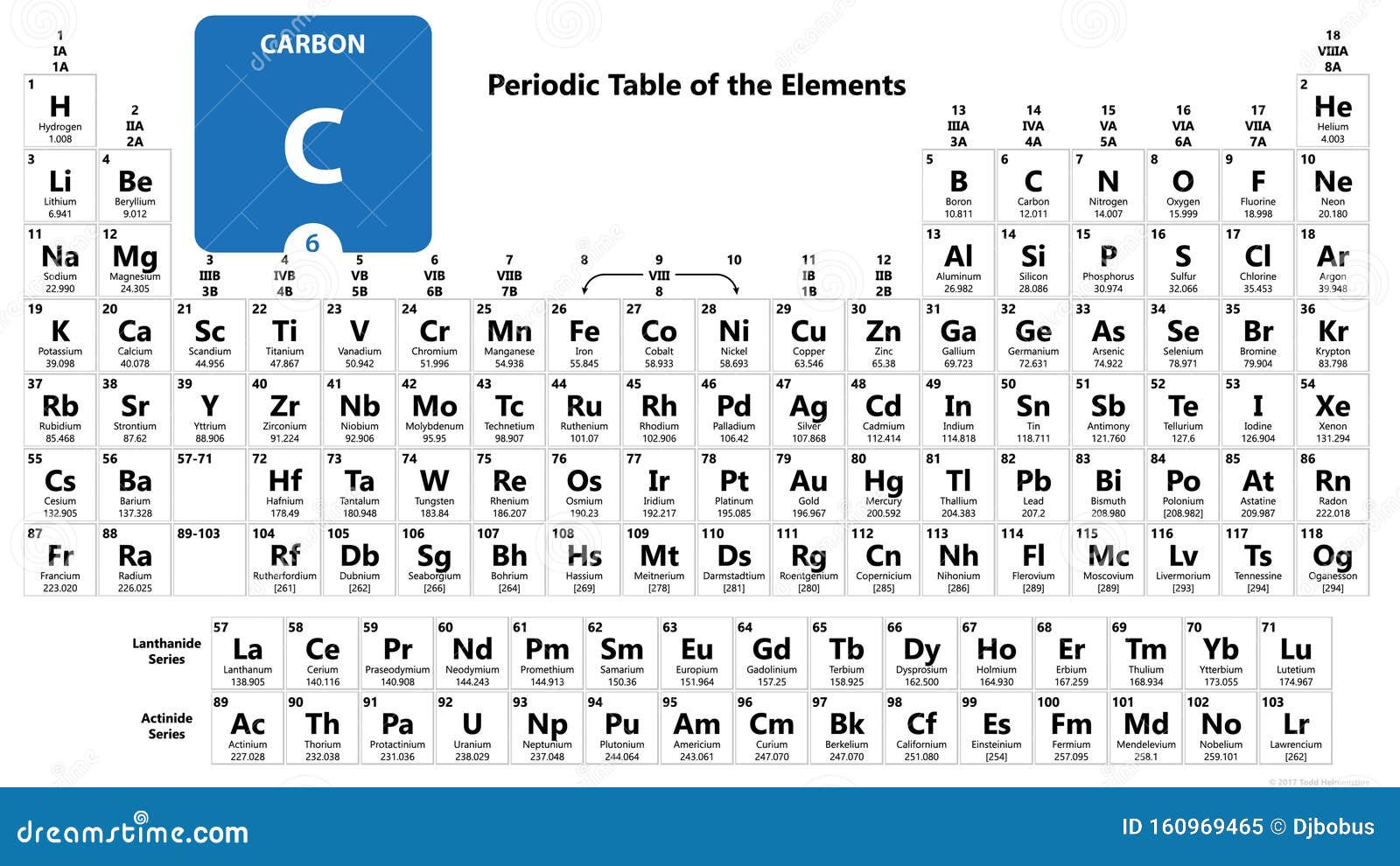
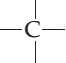
Also, no assurance is given that each item has a chance of being included, making it impossible either to estimate sampling variability or to identify possible bias. In addition, since elements are chosen arbitrarily, there is no way to estimate the probability of any one element being included in the sample. This is often a risky assumption to make in the case of non-probability sampling due to the difficulty of assessing whether the assumption holds. However, in order to draw conclusions about the population from the sample, it must assume that the sample is representative of the population. Since non-probability sampling does not require a complete survey frame, it is a fast, easy and inexpensive way of obtaining data. The mole amounts above represent the number of atoms of each element in the substance's molecular formula.Non-probability sampling is a method of selecting units from a population using a subjective (i.e. Divide all the mole values by this amount:įinally, round each mole amount to the nearest integer to get the final mole ratios: The element with the fewest moles is Calcium, with only 156.19541893308 moles. Use the mass to find the number of moles by dividing the mass by the molar mass (from step 1) of each element:įind the element with the fewest moles. The the molar mass of an element is equal to the atomic weight.Īssume you have 100g of substance to find the mass of each element by multiplying 100g by the percentage: Using a periodic table, find the molar mass of each element. How to find the empirical formula for 37.4% Carbon, 62.6% Calciumįinding the empirical formula of s substance that is 37.4% Carbon (C), 62.6% Calcium (Ca) requires just a few easy steps. You can also ask for help in our chat or forums. Read our article on how to determine empirical and molecular formulas. How To Determine Empirical/Molecular Formulas


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
